Worldwide,
thousands of buoys and floats are
equipped with Argos transmitters,sending information
via the Argos satellite system to help scientists
understand andpredict climate
change. Nearly 6,000 buoys of all types
(drifting, moored, floating ...)
roam the oceans by
collecting data transmitted via Argos on currents, temperature,
salinity. We absolutely had a
partner to help us build our buoy but
especially to provide us with the necessary
hardware to send data via
satellite. This equipment is veryexpensive and the
possibility of using a satellite link could be
achieved through theCNES and society TENUM who
provided the HERA case.
History and evolution of the Argos system and the satellite lisaison
Born in 1978 in a cooperation between the Centre National d'Etudes
Spatiales (CNES), the U.S. Agency for Study of Atmosphere and Ocean
(NOAA) and the U.S. space agency (NASA), he was first used for
safety at sea, such as monitoring of racing sailboats or locate the
survivors. Today, the Argos system is primarily designed to study
and protection of the environment globally.
With low power consumption and a high degree of miniaturization of the
Argos can be attached to birds and mammals and operate several months.
Operation
Argos platforms automatically transmit messages that are received by satellites in low polar orbit.
A platform is a device incorporating a transmitter certified
Argos. A platform periodically sends a message characterized by:
- Frequency of issue (401,650 MHz ± 30 kHz), which must be stable,
because the location calculation is based on measuring the Doppler
effect: this means the change in frequency of the electromagnetic wave
when the source and receiver are moving relative to one another.
- The repetition period is the time interval between two consecutive
shipments of message. It varies from 90 to 200 seconds depending
on the use of the platform,
- The identification number of the platform,
- The data transmitted.
The transmission time of each message is less than a second.
The satellites then transfer messages to ground receiving
stations. The satellite polar orbits at 850 km altitude. The
period of an orbit is about 100 minutes. Each satellite views
simultaneously and at any time all platforms located inside a circle
with a diameter of 5000 km. With the movement of the satellite
ground track of the circle forms a band 5000 km wide that winds around
the Earth via the North and South Poles.
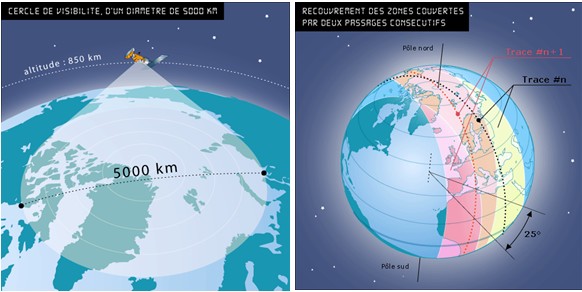
Due to the
rotation of
the Earth, this band shifts with each
revolution of the satelliteabout 25
° west, around the polar axis.
About 50 stations receive data sent from
satellites in real time and transmit
them totreatment centers.
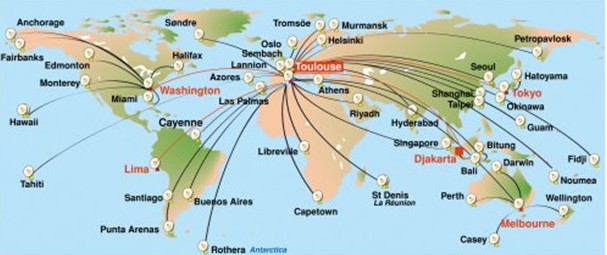
Two processing
centers receive data and distribute them to users,
one in Washingtonthe United States and one
in Toulouse, France. These two centers handle all the data
received. Calculators then proceed to
calculate the location and processing of data
received.
Argos users, which is now
part of our group Argonauts, then
receive their data directlyvia a website. Argos received messages are binary
sequences (ie sequences of 0and 1)
which, once received,
are processed and analyzed.
It
should be noted that we
should not confuse the GPS and ARGOS. GPS is only awhile ARGOS positioning
system is a system of collection and
location data from satellites.
We may summarize all that with this scheme :
